Best Frameworks for CLV Prediction
Compare RFM, cohort modeling, LSTM and MCD neural networks for CLV prediction — trade-offs in accuracy, complexity, and scalability to match your data and resources.
Dec 16, 2025
Predicting Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is key for businesses aiming to focus on long-term customer relationships instead of short-term sales. Four popular frameworks help businesses predict CLV with varying levels of complexity and accuracy:
RFM Analysis: Simple, uses Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value to segment customers. Best for smaller datasets and steady customer behavior.
Cohort Modeling: Groups customers by shared traits (e.g., first purchase date) to track trends over time. Effective for spotting behavior patterns with timestamped data.
LSTM-Based Models: Uses deep learning to process sequential data like transaction histories. Requires large datasets, technical expertise, and high computing power.
MCD-Enhanced Neural Networks: Adds uncertainty estimation to predictions using Monte Carlo dropout. Promising but complex and resource-intensive.
Each method varies in terms of accuracy, complexity, and scalability. The choice depends on your business size, data quality, and technical capacity.
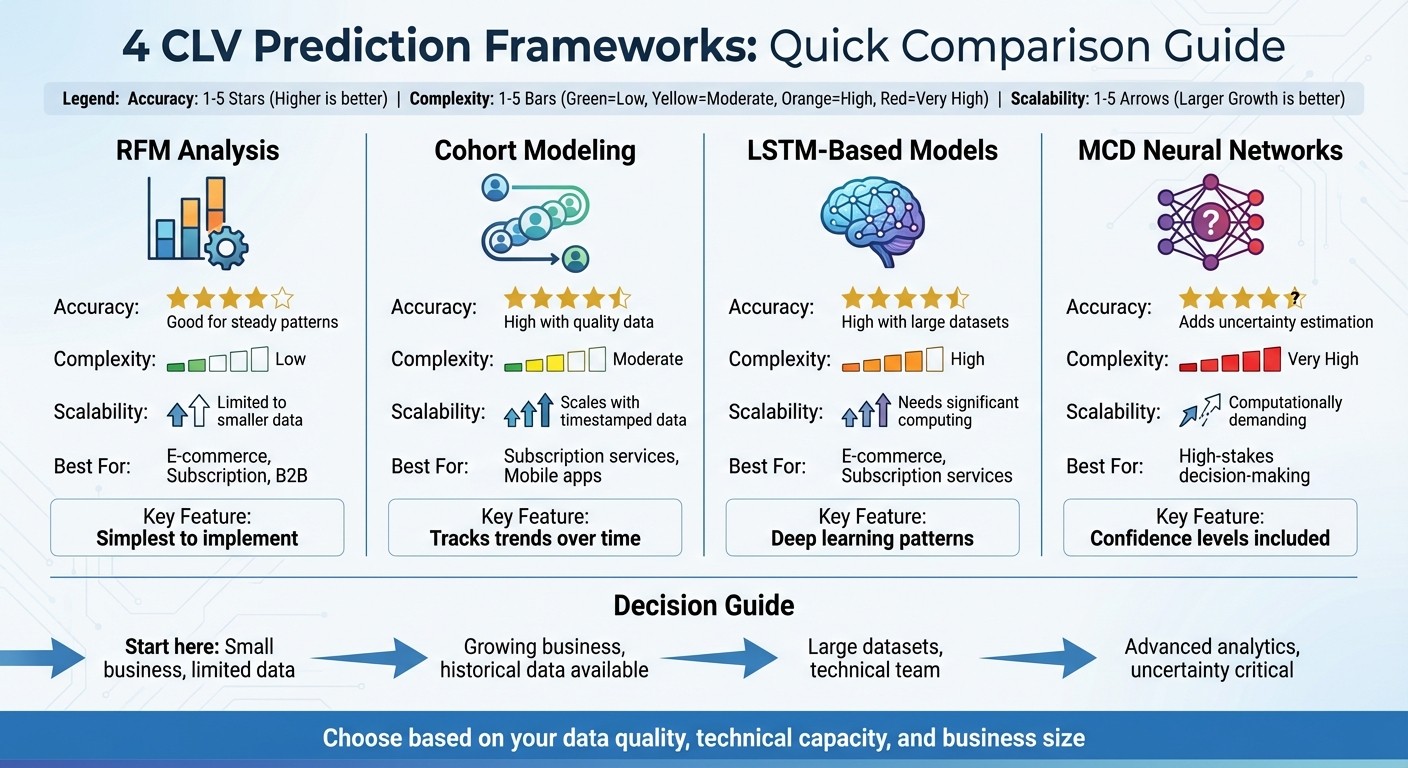
Quick Comparison:
Framework | Accuracy | Complexity | Scalability | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
RFM Analysis | Good for steady behavior patterns | Low | Limited to smaller data | E-commerce, subscription, B2B |
Cohort Modeling | High with quality data | Moderate | Scales with timestamped data | Subscription services, mobile apps |
LSTM-Based Models | High with large datasets | High | Needs significant computing | E-commerce, subscription services |
MCD Neural Networks | Adds uncertainty to predictions | Very High | Computationally demanding | High-stakes decision-making |
The right framework balances your resources with the level of insight you need.
CLV Prediction Frameworks Comparison: Accuracy, Complexity, and Scalability
Measuring Customer Lifetime Value: A Data Scientist's Guide
1. RFM Analysis
RFM Analysis is a method businesses use to estimate customer lifetime value by dividing customers into segments based on three key metrics: Recency (when they last purchased), Frequency (how often they buy), and Monetary value (how much they spend). By scoring customers across these categories, companies can pinpoint their most valuable customer groups and predict how they might behave in the future.
Accuracy
RFM works well for businesses with steady customer behavior patterns. It shines when identifying top-tier customers and those at risk of leaving, based on past purchasing habits. That said, its accuracy can drop in situations where customer behavior becomes erratic or external factors, like market shifts, disrupt patterns. The model relies heavily on the idea that past actions predict future ones - a concept that doesn’t always hold up in fast-changing or uncertain markets. Still, this predictability contributes to its straightforward usability.
Complexity
The simplicity of RFM is one of its greatest advantages. Unlike machine learning models or neural networks, RFM doesn’t require advanced technical knowledge to set up. Marketing teams can calculate RFM scores using basic tools like spreadsheets, making it accessible even for businesses without a dedicated data science team. Scores are typically assigned on a 1-to-5 scale for each metric, creating easy-to-understand customer segments. This uncomplicated setup means companies can implement RFM quickly - sometimes within just a few days.
Scalability
RFM works well for small to medium-sized customer datasets but struggles to handle very large ones. When dealing with hundreds of thousands of records or more, the manual segmentation process becomes unwieldy. Moreover, it lacks the sophistication to capture intricate patterns in complex customer journeys. For companies managing millions of interactions across multiple channels, RFM’s simplicity can turn into a limitation.
Business Use Cases
RFM is widely used across industries. E-commerce retailers often rely on it to focus their marketing budgets, offering exclusive deals to high-value, frequent buyers while using targeted campaigns to win back inactive customers. Subscription services leverage RFM to spot early signs of churn by tracking drops in engagement frequency. For B2B companies with smaller client bases, RFM helps account managers prioritize relationships with the highest revenue potential.
2. Cohort Modeling
Cohort modeling is a technique that groups customers based on shared characteristics - like the time they made their first purchase - and tracks how these groups behave over time. Instead of providing a single, static view of customer value, this approach focuses on trends and patterns, offering a deeper understanding of how customer behavior evolves.
Accuracy
By grouping customers based on their first purchase, cohort modeling helps highlight changes in behavior, such as shifts in retention rates or purchasing patterns. The reliability of these insights depends heavily on having high-quality historical data to work with.
Complexity
Setting up cohort analysis involves a few key steps: defining the criteria for grouping customers, selecting the right tracking intervals (like weekly, monthly, or quarterly), and identifying relevant performance metrics to monitor. While it may seem more complex than simpler, one-time analyses, many modern analytics tools streamline the process. These platforms often include built-in features for setup and visualization, allowing teams to focus on interpreting the data rather than wrestling with technical details.
Scalability
One of the strengths of cohort modeling is its flexibility - it works for businesses of any size. Whether you're looking at a small customer base or analyzing large volumes of transactions, the method remains effective for spotting trends. The key is maintaining accurate, timestamped data. Cloud-based analytics tools make it easy to scale cohort analyses as your data grows.
Business Use Cases
Cohort modeling has practical applications across various industries. For subscription-based businesses, it can reveal trends in customer retention and revenue growth over time. Mobile app developers and retail brands can use it to see how changes in product features or marketing efforts impact customer behavior. These insights help refine strategies and support long-term growth. When combined with other predictive tools, cohort analysis becomes an essential part of strategic customer management.
3. LSTM-Based Models
LSTM-based models leverage deep learning to analyze sequential patterns in customer behavior, making them a tool for predicting Customer Lifetime Value (CLV). However, their performance heavily depends on the quality and availability of historical customer data.
Accuracy
LSTM networks are designed to process sequential data, like transaction histories, to uncover patterns in customer behavior over time. That said, achieving reliable accuracy requires a wealth of high-quality historical data and meticulous tuning. While these models show promise, evidence of their consistent success in real-world applications is still somewhat limited.
Complexity
Implementing LSTM models isn't straightforward. It demands a strong grasp of deep learning concepts, careful selection of features, and ongoing optimization. This level of complexity often translates into a significant investment of time and technical resources.
Scalability
Training LSTM models can be resource-intensive, requiring access to GPU-enabled systems or cloud-based solutions. Additionally, these models need periodic retraining to incorporate new data, which adds to the computational demands.
Business Use Cases
LSTM models are particularly suited for industries with abundant sequential customer data and intricate interactions. For example, businesses in sectors like e-commerce or subscription services can gain a dynamic understanding of customer behavior through these models. While they don't replace traditional methods, they can offer a more nuanced perspective when used alongside them.
4. MCD-Enhanced Neural Networks
MCD-Enhanced Neural Networks present a different approach to customer lifetime value (CLV) prediction by focusing on uncertainty in predictions, setting them apart from traditional and LSTM-based methods.
These networks integrate neural architectures with Monte Carlo dropout, a technique designed to estimate uncertainty in predictions. However, research and real-world applications of this method in CLV forecasting are still in their early stages.
Accuracy
This approach has the potential to generate a range of predictions, reflecting different confidence levels instead of providing a single estimate. However, thorough validation and testing are still needed to confirm its reliability in practice.
Complexity
Developing and deploying these models requires a solid understanding of neural network structures and the mechanics of dropout techniques. Practical examples and benchmarks for CLV prediction using this method are still scarce.
Scalability
One challenge lies in the computational demands. Since the method relies on multiple evaluations to measure uncertainty, processing large datasets could significantly impact performance. The full extent of these demands is not yet fully understood.
Business Use Cases
From a business perspective, the ability to assess prediction uncertainty is appealing, especially for decisions with high stakes. However, concrete examples of how this method can be applied to CLV prediction are still lacking. Businesses exploring this approach should remain cautious and keep an eye on emerging research to gauge its practical value.
Advantages and Disadvantages
When it comes to predicting customer lifetime value (CLV), each framework comes with its own set of strengths and challenges. Here's a quick breakdown to help you weigh your options:
RFM Analysis
RFM Analysis evaluates customers based on recency, frequency, and monetary value. It's straightforward and easy to implement, but its simplicity can be a drawback - it often misses the nuances of changing customer behavior.
Cohort Modeling
Cohort modeling is great for spotting trends in customer retention and spending over time. However, its accuracy heavily depends on having high-quality data and well-defined customer segments.
LSTM-Based Models
These models use deep learning to identify patterns in customer behavior over time, offering more precise predictions. But they come with a cost: you’ll need large datasets, advanced technical skills, and significant computing power.
MCD-Enhanced Neural Networks
Adding Monte Carlo Dropout to neural networks helps estimate the confidence of predictions. While this can be valuable, it also makes the models more complex and resource-intensive.
The right choice boils down to finding a balance between simplicity and the level of analytical depth you need.
Conclusion
Selecting the right Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) framework depends on your business's specific needs and resources. If you're just starting out, RFM Analysis provides a simple and accessible way to begin understanding customer behavior. On the other hand, if you have access to detailed historical data, Cohort Modeling can help identify trends within different customer groups over time.
For companies with advanced data capabilities and technical expertise, more complex models like LSTM-based frameworks or MCD-enhanced neural networks offer deeper insights. However, these advanced methods require significant computing power and specialized knowledge, making them better suited for organizations with the resources to support them.
When choosing a framework, think about your internal capabilities - such as data quality, volume, and technical skills - as well as how precise your predictions need to be. The goal is to strike a balance between your current resources and the insights you want to achieve.
Once you’ve chosen a framework, integrating CLV predictions into your broader strategy can elevate decision-making. By combining these predictions with tools like StratEngineAI, which merges CLV data with market analysis and competitive intelligence, you can create a unified strategic plan. This kind of integration turns raw data into actionable insights, offering a clearer direction for leadership decisions.
Begin with the framework that matches your current resources, and adapt as your data infrastructure and technical expertise grow.
FAQs
What’s the best way to select a customer lifetime value (CLV) prediction framework for my business?
Choosing the best CLV prediction framework hinges on your business priorities, the data you have at hand, and your overall goals. RFM analysis works well when you want to group customers by their transactional behavior - specifically how recently they’ve purchased, how often they buy, and how much they spend. This method is especially useful for spotting your most valuable customers. Meanwhile, cohort modeling shines when you need to study customer behavior and retention trends over specific time periods.
If you’re looking for a more streamlined solution, AI-powered tools like StratEngineAI can be a game-changer. These platforms can automate the selection process, customize insights for your industry, and make decision-making easier. They save you time and help ensure your strategies are grounded in data.
What are the pros and cons of using LSTM models for predicting customer lifetime value (CLV)?
LSTM models bring notable advantages to predicting Customer Lifetime Value (CLV). They're especially good at spotting long-term trends in sequential customer data and can handle inputs of different lengths. This makes them a strong choice for analyzing how customer behavior evolves over time.
That said, they do have their hurdles. Training LSTMs can be resource-intensive, demanding significant computational power. Plus, challenges like vanishing gradients can make the training process tricky, which might affect their scalability or use in real-time scenarios. Still, for businesses equipped with the right computational tools, LSTMs often prove to be a valuable option.
Are MCD-Enhanced Neural Networks more effective than traditional methods for predicting customer lifetime value (CLV)?
While MCD-Enhanced Neural Networks bring advanced modeling techniques to the table and hold potential for improving customer lifetime value (CLV) predictions, there’s no conclusive proof that they consistently outperform traditional methods like RFM analysis or cohort modeling. The effectiveness of these approaches often depends on the specific use case and the quality of the data being used, and research in this area is still evolving.
That said, traditional methods continue to be a dependable choice. Their simplicity and track record of effectiveness make them especially valuable in situations where cutting-edge AI tools are either unavailable or not yet fine-tuned for the task at hand.






