
How AI Improves KPI Forecasting Accuracy
AI cleans and unifies data, detects complex patterns, and updates forecasts in real time to cut errors, speed processing, and improve KPI accuracy and ROI.
Dec 29, 2025
AI makes KPI forecasting faster, more precise, and less prone to errors by addressing the limitations of manual methods. It analyzes large datasets, detects patterns, and continuously updates predictions, helping businesses make better decisions and automate strategic briefs in minutes. Here's what you need to know:
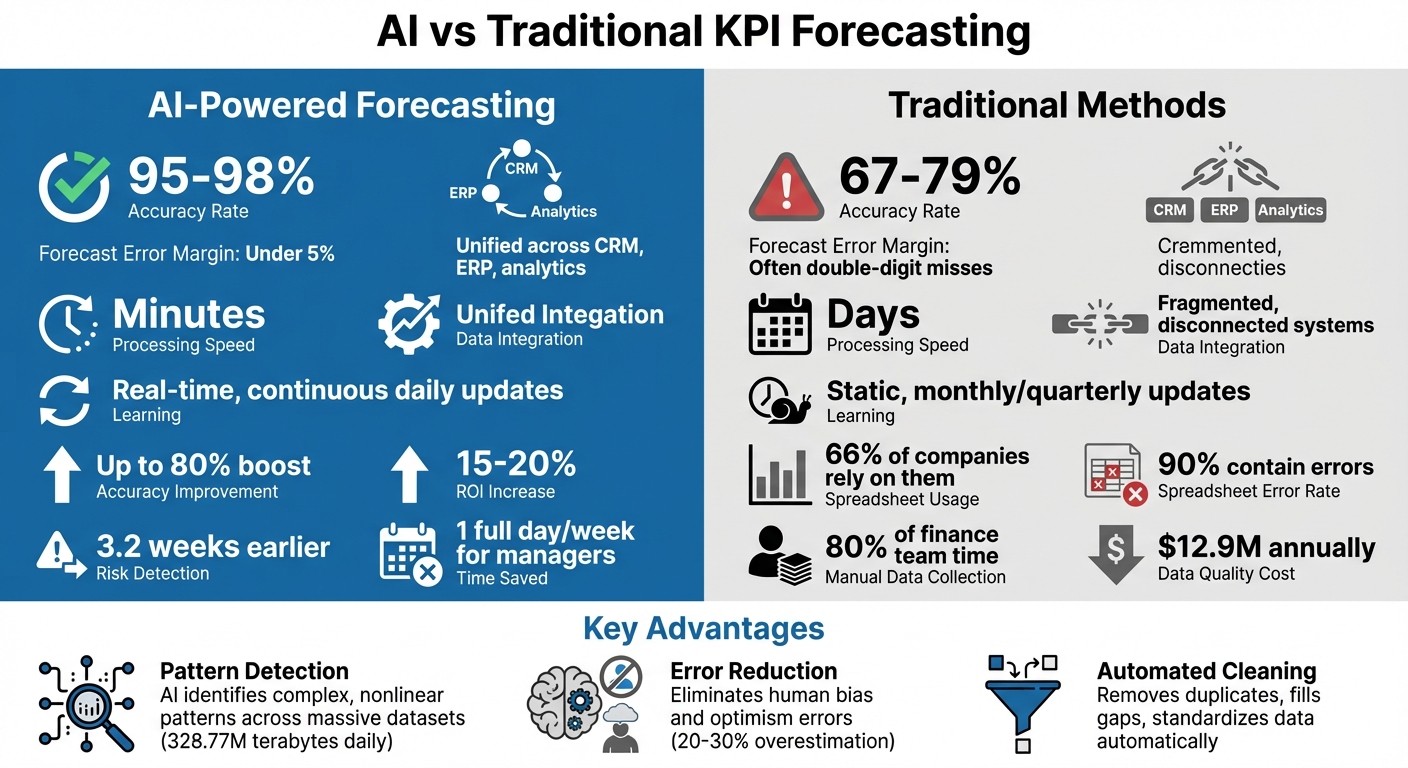
Higher Accuracy: AI reduces forecast errors to under 5%, compared to 70–79% accuracy with manual methods.
Faster Processing: Tasks that took days can now be completed in minutes.
Unified Data: AI integrates fragmented data from systems like CRM and ERP, eliminating inconsistencies.
Real-Time Updates: AI learns daily, ensuring forecasts stay relevant to market changes.
Error Reduction: By automating data cleaning and analysis, AI removes human biases and errors.
Companies using AI forecasting report up to an 80% improvement in accuracy, a 15–20% boost in ROI, and significant cost savings across sales, inventory, and financial planning.
AI doesn’t replace human judgment but enhances it, providing actionable insights for smarter decision-making.
AI vs Traditional KPI Forecasting: Accuracy, Speed, and Performance Comparison
Boosting Forecast Accuracy with External Data and AI Techniques
Problems with Traditional KPI Forecasting
Traditional forecasting methods often fall short, leading to inaccurate predictions and costly mistakes. Below, we break down some of the key challenges that hinder these methods.
Fragmented Data Sources
One of the biggest hurdles to reliable KPI forecasting is fragmented data. Many organizations rely on disconnected systems - like CRM platforms, ERP software, and finance tools - that don’t communicate effectively. This lack of integration creates inconsistencies, such as data gaps, duplicates, and mismatches, all of which erode the accuracy of forecasts.
"Disconnected systems such as separate CRM, ERP, and analytics tools often result in data inconsistencies. When data is not consolidated, it creates gaps or duplicates, making it difficult to produce a clear, unified view of trends." - Ramya S., Zipteams [1]
A striking example of the damage caused by inconsistent data is NASA's $125 million loss of the Mars Climate Orbiter. The error occurred because one team used metric measurements while another used English units [5]. This shows how fragmented data can lead to catastrophic results.
Subjective Judgment Errors
Human judgment introduces bias into traditional forecasting, which can skew results significantly. For instance, sales representatives often overestimate their chances of closing deals by 20–30% due to optimism bias [6]. On top of this, managers relying on gut instincts are prone to confirmation bias, further distorting predictions.
"Decisions based on 'gut feelings' may overlook key factors or introduce bias, leading to inaccurate predictions." - Ramya S., Zipteams [1]
Manual processes only add to the problem. Finance teams, for example, spend up to 80% of their time manually collecting and combining data [4]. Managers often waste over six hours a week auditing call recordings and cross-referencing emails because CRM data is incomplete or outdated [6]. This "manager tax" not only drains time but also increases the likelihood of errors.
Difficulty Handling Large Datasets
Traditional spreadsheet-based methods simply can’t keep up with today’s massive data volumes. With over 328.77 million terabytes of data generated daily [5], manual systems lack the speed and capacity to process information for real-time decision-making.
Despite this, 66% of companies still rely on spreadsheets for forecasting. The problem? Nearly 90% of spreadsheets contain errors, and only 20% of sales teams achieve forecast accuracy within 5% of actual results. Traditional methods typically hover between 70% and 79% accuracy at best [4].
Poor data quality costs businesses an average of $12.9 million each year [5]. Shockingly, 80% of collected data remains "dark", meaning it’s never analyzed or used for decision-making. These inefficiencies can result in forecasts missing actual outcomes by double digits [2], leaving executives without the insights they need to make timely adjustments or allocate resources effectively.
These challenges highlight the need for more advanced, AI-powered forecasting solutions. For more business innovation insights, explore our latest strategy guides.
AI Methods That Improve KPI Forecasting
AI tackles the weaknesses of traditional forecasting by offering three game-changing capabilities: automated data cleaning and integration, pattern detection at scale with machine learning, and continuous, real-time learning. Together, these tools deliver predictions that are not only more precise but also easier to act on.
Automated Data Cleaning and Integration
AI systems excel at tidying up messy data. They standardize information from scattered sources, remove duplicates, and fill in missing pieces, ensuring the forecast remains reliable. By automating the integration of data from platforms like CRM, ERP, and marketing tools, AI creates a single, unified view of your business.
"Treat Data As A Product - Standardize definitions, clean outliers, and ensure reliable pipelines from your CRM, marketing platforms, finance systems, and product analytics." - The Pedowitz Group [2]
When companies treat their data as a formal product - complete with consistent definitions and automated cleaning - they see tangible improvements. It’s simple: cleaner data leads to sharper forecasts [1]. From there, machine learning takes things a step further, uncovering patterns that are often hidden in the noise.
Machine Learning for Pattern Detection
Machine learning (ML) thrives where traditional models fall short. It identifies complex, nonlinear patterns by analyzing factors like seasonality, promotions, and even broader economic trends. Companies using advanced AI forecasting have reported up to an 80% boost in forecast accuracy [3], while AI-powered inventory management has cut excess inventory by 63% [3].
ML doesn’t stop at structured data. Using Natural Language Processing (NLP), it can analyze unstructured sources like customer reviews or social media chatter, turning them into early warnings for demand changes [1]. The secret lies in feature engineering - converting business metrics like campaign performance, pricing tiers, or channel mix into inputs that help the model zero in on what truly drives your KPIs [2].
Real-Time Learning Systems
Unlike static forecasts that are updated monthly or quarterly, AI systems continuously learn and update predictions daily. This keeps forecasts aligned with market changes rather than letting them grow stale between review cycles. Modern tools even provide probability ranges and confidence intervals to give a clearer picture of forecast uncertainty [2].
Real-time systems can also send automatic alerts when actual performance veers off from predictions by a set margin, like 5%. This allows businesses to make quick adjustments instead of waiting for the next planning session [1]. However, these systems aren’t entirely hands-off - AI models need to be retrained at least quarterly to stay accurate as conditions shift [1].
How to Implement AI for KPI Forecasting
After looking at the challenges of traditional forecasting and the advantages AI brings, it’s clear that implementing AI for KPI forecasting requires a structured approach. This process involves four main steps: data preparation, model selection and training, accuracy testing, and deployment with ongoing monitoring. Each step builds on the previous one, ensuring your forecasts are both reliable and actionable.
Step 1: Gather and Prepare Data
Begin by creating a single source of truth across your organization. This means standardizing definitions so terms like "revenue", "customer", and "conversion" mean the same across departments like sales, marketing, and finance. Pull data from systems such as CRM, ERP, marketing platforms, and product analytics, then unify it to get a comprehensive view of customer behavior [1][2].
Next, clean the data by addressing duplicates, filling in missing values, and managing outliers. Wherever possible, automate this process to save time and ensure accuracy [1].
Finally, engineer features that reflect key business drivers. These might include lagged metrics (like last month’s performance), seasonality indicators (e.g., holiday periods), campaign markers (timing of promotions), and pricing tiers. These added features help the AI model understand what truly influences your KPIs [2].
Once your data is unified, cleaned, and enhanced with features, you’re ready to move on to selecting and training AI models.
Step 2: Choose and Train AI Models
The type of AI model you choose will depend on the complexity of your data. For steady patterns with clear seasonal trends, time-series models are often the best fit. If your data involves multiple factors influencing outcomes, gradient-boosted trees are more appropriate. For highly complex, non-linear data, neural networks can provide deeper insights [1][2]. Many organizations start with simpler time-series models and gradually adopt more advanced techniques as their data capabilities grow.
Train your chosen model using historical data that includes the engineered features - like promotions, pricing changes, or macroeconomic indicators. For example, in 2024, Walmart used machine learning to analyze point-of-sale data from individual stores and regions, enabling them to predict demand more precisely. This reduced stockouts and cut down on excess inventory costs [1]. Similarly, Amazon analyzed customer browsing history, social media trends, and past purchases to forecast demand by customer segment, leading to fewer shortages and faster inventory turnover [1].
"AI is most effective when it augments human judgment rather than replacing it. Models excel at finding patterns in large datasets, while humans provide strategic context." - The Pedowitz Group [2]
To keep your models accurate, retrain them at least quarterly. This helps account for changing market conditions and seasonal variations [1][2].
Step 3: Test Forecast Accuracy
Before deploying your model, validate its performance using holdout samples - historical data that wasn’t included during training. This backtesting helps reveal how well the model handles real-world scenarios [2]. Organizations often aim for a forecast margin of error within 5% [1].
Use a mix of metrics to evaluate accuracy. Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) measures the average size of errors in percentage terms. Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) highlights larger errors by giving them more weight, and forecast bias checks if the model consistently over-predicts or under-predicts [1]. Test the model across various time periods and conditions to ensure it remains reliable under different scenarios.
Step 4: Deploy and Track Performance
Once validated, integrate your forecasts directly into the tools your teams already use - whether it’s planning software, dashboards, or revenue operations workflows [2]. Set up automated monitoring to track forecast changes and send alerts when actual performance deviates from predictions by a set threshold, often around 5% [1].
Regular maintenance is crucial. Keep an eye out for model drift, which happens when predictive accuracy declines because data patterns evolve. This could result from market changes, competitor actions, or shifting customer preferences [2].
Equally important is ensuring that forecasts are accessible and actionable. When integrated into the systems where decisions are made, forecasts are more likely to be used effectively. The ultimate goal isn’t just better predictions - it’s making informed decisions based on those predictions.
With your AI system in place and monitored, the next step is to evaluate how it improves your forecasting accuracy.
How to Measure AI Forecasting Improvements
Once you've deployed an AI forecasting model, the next step is to evaluate its effectiveness. This involves comparing the model's predictions against actual outcomes and tracking specific metrics that quantify errors. Companies that adopt data-driven forecasting approaches have reported a boost in ROI by 15–20% [1]. These metrics serve as a bridge between improved modeling and actionable business decisions.
Key Forecasting Accuracy Metrics
There are four primary metrics to assess how well your AI model is performing. Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) calculates the average percentage difference between predicted and actual outcomes. Mean Absolute Error (MAE) focuses on the average size of prediction errors, ignoring whether the errors are positive or negative. Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), on the other hand, emphasizes larger errors, making it useful for identifying significant deviations [1].
Another critical metric is forecast bias, which shows whether your model consistently over-predicts or under-predicts. For instance, repeated overestimations may indicate a systematic bias that needs adjustment [1]. Companies with advanced forecasting systems often aim for a forecast error margin of just 5% [1].
Beyond these standard metrics, it's essential to keep an eye on model drift. Over time, your AI model's accuracy may decline as real-world conditions shift away from the data it was trained on. Factors like changing market trends or evolving customer behaviors can contribute to this drift [2]. Regular monitoring helps catch these issues early, minimizing their impact on decision-making.
AI vs. Traditional Forecasting Performance
When comparing AI-driven forecasting to traditional methods, the differences in speed, accuracy, and adaptability become clear. Traditional models work well in stable environments but struggle when markets change rapidly or when multiple complex factors interact [2]. AI, however, excels in identifying non-linear patterns and can update predictions in real time as new data becomes available, making it far more flexible [2].
While traditional expert judgment can provide valuable insights, especially in markets with limited historical data, it often lacks consistency and scalability across diverse product lines or regions [2]. AI models address these challenges by reducing inconsistencies while allowing human oversight to add strategic context.
"AI is most effective when it augments human judgment rather than replacing it" [2].
To compare forecasting methods, use holdout samples - historical data that wasn't used during training - to test how well each approach predicts known outcomes. This backtesting process can reveal which method delivers more reliable forecasts under different conditions [2]. Additionally, automated alerts for forecast deviations can help your team quickly identify when AI models outperform manual methods or when additional human insights are necessary [1]. These tools highlight how AI-driven forecasting supports better strategic decision-making.
Real-World Applications of AI KPI Forecasting
AI forecasting turns theoretical concepts into practical tools that drive results across industries. Businesses rely on these advanced systems to make quicker, more informed decisions that directly influence their profitability. Let’s look at how AI is reshaping key business functions.
Example: Sales Revenue Forecasting
In traditional sales processes, pipeline reviews often depend on manual input, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. AI steps in to dramatically improve accuracy by analyzing conversation patterns to assess buying intent and flagging opportunities at risk. For instance, AI can:
Analyze sales calls using intent recognition and sentiment analysis.
Integrate CRM data for a comprehensive view of prospects.
Automatically detect BANT signals (Budget, Authority, Need, and Timeline) during conversations.
Segment forecasts by region, product line, or customer group for more tailored insights.
This same precision extends to inventory operations, where AI uses granular point-of-sale data to fine-tune adjustments.
Example: Inventory Management
Managing inventory requires juggling a range of factors, such as historical sales, seasonal trends, customer behavior, and external influences like weather or economic changes. AI thrives in this complex environment by analyzing point-of-sale data down to individual stores or customer segments. Its real-time processing capabilities allow businesses to respond quickly to demand spikes while automating up to 50% of planning tasks. Additionally, AI applies data smoothing to eliminate anomalies like one-off promotions and incorporates external data - such as weather forecasts - to improve seasonal demand predictions.
The financial sector also benefits from AI’s ability to handle intricate datasets and uncover patterns that traditional methods might miss.
Example: Financial Performance Projections
Accurate financial forecasting is essential for budgeting, managing risks, and making executive decisions and customizing SWOT with AI. Companies using AI-driven forecasts have seen a 15–20% improvement in ROI, with many aiming for forecast error margins below 5%. AI models are retrained quarterly to adapt to market changes and seasonal variations, ensuring their predictions stay relevant. Automated alerts for deviations in forecasts enable companies to take corrective action immediately. These AI-powered financial insights help leaders make smarter decisions about resource allocation and risk management, ensuring their strategies are both data-driven and effective [1].
Best Practices for AI Forecasting with StratEngineAI

To get the most out of AI-driven forecasts, it's crucial to align predictions with your business goals. Here's how you can make AI-powered KPI forecasts work harder for your organization.
Connect Forecasts to Business Objectives
Start by clearly defining what you're trying to achieve. Are you forecasting revenue to plan hiring needs? Or perhaps you're predicting customer churn to decide on retention budgets? Each goal requires a unique approach - different timeframes, levels of detail, and data inputs. When forecasts are tightly linked to strategic decisions, businesses can boost ROI by 15–20% [1].
Integrating your AI tools with essential systems like CRM and ERP ensures consistency. This creates a single source of truth, giving you a unified view of customer behavior and market trends [1]. Such integration eliminates data silos, making your strategic decisions more reliable.
Instead of relying on a single prediction, consider presenting forecasts as ranges or probability scenarios. This approach helps decision-makers weigh both potential gains and risks, making it easier to allocate resources effectively and mitigate uncertainties [2]. Leading organizations aim for a forecasting margin of error within 5%, underscoring the importance of aligning forecasts with business priorities [1].
To make these insights actionable, use structured planning tools that integrate forecasts into your broader strategy.
Use StratEngineAI's Planning Frameworks
StratEngineAI offers over 20 strategic frameworks - like SWOT, Porter's Five Forces, and financial models - that help you turn AI forecasts into actionable plans. These tools allow you to embed KPI predictions into a larger strategic context. For instance, when generating a strategic brief, the platform automatically incorporates forecast data into market analysis and competitive insights, creating a narrative that executives can act on immediately.
Automated alerts are another powerful feature. They notify you when actual performance deviates from forecasts, enabling swift adjustments [1]. This real-time feedback loop ensures your strategy remains agile and prevents minor forecast errors from snowballing into bigger problems.
Keep AI Models Current
AI models can lose accuracy over time due to changing market conditions - a phenomenon known as "data drift." To keep your forecasts reliable, schedule regular validation and retraining of your models, ideally every quarter [1][2].
"The best practice is to combine scheduled retraining with model performance monitoring to be able to detect quality decay or data drift." – Elena Samuylova, CEO and Co-founder of Evidently AI [5]
Track metrics like Mean Absolute Error (MAE) or Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) monthly or quarterly. If accuracy dips - say, your margin of error exceeds 5% - initiate an immediate review. Businesses that consistently review and refine their forecasts report a 67% improvement in both accuracy and revenue outcomes [5]. Regular maintenance and updates are key to sustaining the effectiveness of your AI models.
Conclusion
AI has redefined forecasting, turning it from an educated guess into a precise, data-driven process. Traditional methods, often reliant on spreadsheets and subjective judgment, typically achieve accuracy rates between 67% and 79%. In comparison, AI-powered systems boast accuracy levels of 95% to 98% by detecting nonlinear patterns, merging fragmented datasets, and continuously learning from incoming information [4][6]. This leap in precision empowers businesses to make smarter decisions, with companies using AI-driven forecasting seeing a 15–20% increase in ROI [1] and being 10% more likely to achieve year-over-year revenue growth [4]. Such accuracy also enhances a company's ability to quickly spot risks and seize opportunities.
For instance, AI can identify risks up to 3.2 weeks earlier than manual methods and save managers the equivalent of one full day per week previously spent on auditing tasks [6]. This proactive approach strengthens strategic planning, allowing businesses to respond faster to market changes. As Michael Schrage from MIT Sloan School of Management highlights:
"We learned that smart leaderships see AI as essential to making their KPIs smarter, more predictive, and more insightful" [5].
StratEngineAI takes this a step further by embedding forecasts directly into strategic planning. It transforms raw data into actionable insights and polished, boardroom-ready briefs. With its natural language interface, even non-technical team members can query data in plain English. This accessibility spreads insights across Finance, Operations, and Sales [5], enabling faster, more informed decisions in real time.
FAQs
How does AI improve the accuracy of KPI forecasting?
AI takes KPI forecasting to the next level by diving deep into complex historical and real-time data patterns. It doesn’t just analyze them - it learns from them automatically, delivering predictions that are far more reliable. Unlike old-school methods that depend on static spreadsheets, AI generates dynamic, adaptable forecasts. These forecasts adjust as new data comes in, cutting down errors by an impressive 20–50%.
What’s more, AI plays a crucial role in improving data quality. It spots inconsistencies and reduces the impact of human biases, ensuring the forecasts are built on clean, objective inputs. The result? Smarter decision-making and a sharper focus on achieving business goals.
How can AI enhance the accuracy of KPI forecasting, and what steps are involved?
AI has the potential to boost the accuracy of KPI forecasting by processing vast datasets, spotting trends, and delivering predictions with limited human bias. To get started with AI-driven KPI forecasting, first, pinpoint the specific KPI you want to predict - whether it’s revenue, customer churn, or something else - and set the desired time frame for your forecast. Then, gather historical data, clean it up by removing outliers, and ensure it’s properly standardized.
The next step is to create relevant features from your dataset. These could include factors like seasonal patterns or broader economic trends, which help the AI model identify the key influences on your KPI. From there, select a machine-learning model suited to your needs. Time-series algorithms or neural networks are common choices, depending on the complexity of your data and goals. Evaluate your model’s accuracy using metrics such as Mean Absolute Error (MAE) or Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) to ensure reliable results.
Once your model is performing well, integrate it into your business intelligence tools for real-time forecasting. Keep a close eye on its performance, regularly update it with fresh data, and fine-tune its outputs to maintain precision as conditions change. By following this process, businesses can leverage AI to make smarter, data-backed decisions with greater confidence.
How can AI forecasting help meet specific business goals?
AI forecasting helps businesses achieve their goals by concentrating on clear outcomes, like boosting revenue, optimizing demand, or minimizing customer churn. To make this work, companies need to pinpoint the main factors driving these objectives, ensure access to reliable, real-time data, and apply AI models to deliver precise predictions. These forecasts enable leaders to make smarter choices about resource allocation, pricing, and long-term strategies.
When AI forecasting aligns with your business priorities, it turns insights into practical strategies, keeping your organization flexible and competitive in a fast-evolving market.






