
Custom AI Tools: Privacy Checklist for C-Suite
A 12-point privacy checklist for executives to vet custom AI vendors: encryption, access controls, data residency, governance, incident response, and audits.
Dec 24, 2025
AI tools are now deeply embedded in business operations, handling sensitive tasks like strategic brief development and confidential data analysis. But with this reliance comes growing privacy risks.
Here’s what you need to know:
Data Risks: Many AI platforms use sensitive organizational data for model training, potentially exposing proprietary information.
Vendor Practices: Evaluate encryption, certifications (e.g., SOC 2, ISO 27001), and data residency policies before signing contracts.
Access Controls: Implement role-based access and multi-factor authentication to limit exposure.
Governance: Establish oversight committees, conduct audits, and enforce strict policies to manage AI risks.
Incident Response: Develop AI-specific plans to address breaches and monitor vendor compliance.
A 12-point checklist ensures vendors meet privacy standards, covering encryption, data deletion, retention policies, and transparency. This approach safeguards sensitive data while maintaining compliance with regulations like GDPR and the EU AI Act.
Read on for actionable steps to protect your organization.
How to Keep Company Data Secure When Using AI (Top Strategies)
Vendor Security Practices
Before entering into a contract with any AI vendor, it's crucial for executives to take a hard look at the security measures that safeguard their organization's sensitive data as they build data-driven strategies. This involves digging into the vendor's technical practices, certifications, and data handling protocols. After all, cybersecurity tops the list of risks that boards prioritize and remains the No. 1 focus area for audit committee education [7]. The evaluation process should center on three main areas: encryption standards that protect data throughout its lifecycle, compliance certifications that verify adherence to industry standards, and data residency policies that align with regional legal requirements. By conducting a thorough security assessment, organizations can meet procurement standards while reducing reputational risks. These key pillars - encryption, certifications, and residency - are essential for adopting AI securely.
Data Encryption Standards
Encryption is your first line of defense against data breaches. It's essential to confirm that vendors use encryption both at rest and in transit - this ensures data is protected while stored on servers and during transmission between systems. Vendors should also implement zero data retention policies to prevent unauthorized use of data for model training. Ask vendors directly about their encryption protocols and confirm they align with current industry best practices. With the rise of autonomous AI systems, real-time encryption has become even more critical. Gartner estimates that 1 in 3 enterprise software applications will feature agentic AI by 2028 [6]. To ensure compliance, request documentation proving that the vendor’s encryption methods have been validated through third-party security audits [1].
Compliance Certifications
Certifications are a concrete way to verify a vendor's commitment to security. Look for certifications like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and ISO/IEC 42001 (specific to Artificial Intelligence Management Systems). Vendors should also adhere to frameworks such as the NIST AI Risk Management Framework and ENISA's Multilayer Framework for AI [1][8]. If your organization operates in the European Union, ensure the vendor complies with the EU AI Act and GDPR, while those handling data from California residents should confirm compliance with CCPA [8].
Request proof of third-party audits conducted within the past year. Vendors should maintain detailed audit logs and integrate AI security measures into their broader Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) [8]. If a vendor cannot provide up-to-date certifications or audit reports, it’s a warning sign that warrants further scrutiny.
Understanding where and how data is stored is just as important as certifications.
Data Residency and Storage
The physical location of data storage has both legal and security implications. Verify where the vendor stores your data and whether they offer residency options that meet your regulatory needs. Contracts should clearly outline data handling, storage, and retention policies, as well as what happens to your data when the contract ends [1]. Geographic boundaries play a significant role in compliance, as different jurisdictions enforce varying levels of data protection. For instance, 80% to 90% of iPhone users opt out of tracking when given the choice, highlighting the growing demand for data privacy [5]. This same level of scrutiny should apply to enterprise data.
Ask vendors how data is encrypted, stored, and accessed by their AI systems to ensure compliance with geographic restrictions [6]. It’s also essential to audit upstream suppliers to identify vulnerabilities in the storage chain [1]. Many vendors rely on third-party hosting providers, so understanding the entire data storage ecosystem is critical. Contracts should specify that data must be securely deleted or returned after the agreement ends [1]. For organizations subject to the EU's Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), vendors must demonstrate compliance with these operational standards [6].
Data Handling and Access Controls
Once you've evaluated vendor security practices, the next step is to secure data access by implementing strict user permissions. Encryption alone isn't enough to protect sensitive information if access isn't tightly controlled. As Stoel Rives LLP puts it:
Organizations are now expected to actively manage AI-related risks, not just react to them.
This means putting in place technical measures that limit data exposure and ensure access is granted only to the right individuals at the right time.
A good starting point is establishing an AI Oversight Committee. This team should include representatives from legal, IT, and privacy departments to define clear access roles and responsibilities. By bringing together these perspectives, you can align access controls with technical capabilities and regulatory obligations. The committee should also conduct audits across departments to identify all AI tools in use - including any informal or unauthorized ones - and document who has access to sensitive data. These steps, combined with vendor security measures, create a more comprehensive data protection framework.
Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC)
Role-based access controls (RBAC) are an effective way to restrict access to data based on specific job roles. For example, developers, deployers, and end-users should only have access to the data necessary for their specific tasks. This prevents overexposure of sensitive information. To ensure consistency, establish centralized policies covering data handling, access, storage, and retention. When working with third-party AI suppliers, complement these internal measures with contractual agreements that enforce similar standards.
Additionally, implement security logs to track key user actions, retaining these logs for 90 days to support monitoring and compliance efforts [3]. Pair these role-based restrictions with strong identity verification protocols for added protection.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Adding multi-factor authentication (MFA) strengthens security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods before accessing AI systems. This extra layer of protection not only limits unauthorized access but also ensures compliance with regulations like the EU AI Act and GDPR. Conduct audits to confirm that MFA is consistently applied across all AI tools in your organization.
It's equally important to verify that third-party vendors and foundational model providers have adopted MFA and other robust access controls. Ensuring uniform implementation of MFA across all systems reduces vulnerabilities and builds trust in your security practices.
Data Minimization and Anonymization
Even with controlled access in place, it's essential to limit data exposure through minimization and anonymization. Collect and retain only the data that is absolutely necessary for your AI tools to function. For instance, a 90-day retention schedule can help reduce the risk of sensitive data being exposed over time.
Use tokenization to replace sensitive data during model training, and partially mask identifiers like IP addresses in access logs to enhance privacy without sacrificing monitoring capabilities. When possible, rely on synthetic or augmented datasets for training and testing to minimize the use of real-world sensitive information. For data accessed via third-party APIs, ensure it is used strictly for its intended purpose and not for training generalized AI models. Finally, document the entire data lifecycle - from ingestion to inference - to meet explainability and provenance requirements [9].
Governance and Compliance Frameworks
Building strong access controls and data handling practices is only part of the equation - you need a governance structure to ensure these safeguards are consistently upheld. Even the best protections are ineffective without clear oversight. The solution? Assign specific executives to take ownership of AI privacy decisions and establish formal processes for evaluating tools before they’re put to use.
An effective starting point is forming an AI Oversight Committee. This team should bring together leaders from legal, privacy, compliance, IT, and business departments. Regular meetings are essential for reviewing internal policies, evaluating procurement practices, and ensuring all AI tools comply with regulatory requirements and ethical principles [1][10]. As Stoel Rives LLP points out:
AI readiness is not simply about regulatory compliance. Organizations with clear AI governance, auditability, and transparency protocols are better positioned to meet procurement standards, attract enterprise clients, and mitigate reputational risk [1].
This governance framework ensures technical controls are paired with clear executive accountability.
C-Suite Accountability
To ensure smooth oversight of AI systems, designate specific executives to be accountable for them. This isn’t about handing out new titles - it’s about clearly defining who is responsible for compliance. When privacy issues arise, it should be immediately clear which executive is in charge of the affected AI tool or system. This accountability model speeds up decision-making and ensures someone is always monitoring how sensitive data is handled.
Consider establishing a board-level strategy committee tasked with overseeing mid- and long-term AI decisions. This ensures leadership remains engaged and accountable for the organization’s AI initiatives.
Policy Development and Audits
Develop policies that explicitly ban the use of unapproved AI tools. This tackles the growing issue of "shadow AI", where employees use informal tools without IT’s knowledge, creating serious risks of data breaches [1]. Conduct a company-wide audit to identify all AI tools currently in use - both formal and informal. Document who has access to these tools, classify them by risk level (using frameworks like the EU AI Act), and ensure high-risk tools are closely monitored [1].
Integrate privacy and cybersecurity reviews into procurement processes [1]. Before any tool gets the green light, it should pass a thorough review by the AI Oversight Committee. Regular audits are also critical to confirm that systems are functioning as intended, avoiding bias, and safeguarding sensitive data [1]. Keep detailed records of governance decisions and risk assessments to stay prepared for regulatory inspections [1].
Once policies are in place, the next step is to ensure you’re ready to respond swiftly to any incidents.
Incident Response Planning
Develop an AI-specific incident response plan that addresses vulnerabilities unique to AI, such as model drift and data leaks [1][2]. Clearly define escalation paths, specifying which C-suite executives are responsible for AI privacy compliance during an active incident [1].
Your plan should also include steps for auditing and addressing breaches involving upstream AI vendors or foundational model providers [1]. For generative AI tools, incorporate human reviews to catch errors before they cause significant damage [2]. Real-time monitoring is essential to detect anomalies like model drift or security breaches. Track key metrics, such as Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) and detection time, to measure the effectiveness of your response efforts [2]. The quicker you act, the less data is compromised, and the less harm is done to your organization’s reputation.
Monitoring, Logging, and Incident Response
Keeping AI systems secure and private requires constant vigilance. Without ongoing monitoring, potential privacy risks can slip through unnoticed. By combining continuous monitoring with robust access controls and governance, organizations can address threats before they escalate, forming a solid foundation for proactive risk management [1].
Audit Logs
Capturing every AI action - like viewing, creating, updating, or exporting data - along with timestamps, user agents, and status, is essential [3]. These logs are your go-to resource for tracking data usage and spotting unauthorized access. It's recommended to retain these logs for 90 days [3].
To maintain privacy while ensuring visibility, consider masking sensitive details, such as IP addresses, within your logs [3]. Work closely with your legal, privacy, and IT teams to align your logging practices with regulations like GDPR or CCPA [1]. Importantly, logs should only be used for purposes such as security monitoring, troubleshooting, and detecting fraud - not for unrelated activities [3].
Real-Time Monitoring
Real-time monitoring tools provide instant oversight of AI interactions, flagging anomalies as they occur [3]. These tools can track activities like generating strategic frameworks, exporting presentations, or entering sensitive prompts [3]. Human oversight remains a critical layer of protection, ensuring AI systems operate correctly and helping to address any biases [1].
Your monitoring efforts shouldn’t stop at internal systems. Extend them to include upstream AI suppliers and third-party vendors [1]. If a breach happens at a vendor’s end, you need to be informed immediately. Regularly audit their security measures and incident response processes to confirm they align with your standards [1].
Escalation Protocols
When monitoring systems detect a potential issue, it’s essential to have a clear plan in place. Assign specific executives to handle AI privacy incidents and outline their responsibilities in detail [1]. Audit logs should be integrated into your incident response protocols so that any flagged suspicious activity triggers an immediate investigation [1]. Keep track of performance metrics like Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) and detection time to evaluate how well your team handles incidents [2].
This approach to monitoring and incident response not only strengthens your overall privacy strategy but also supports effective training and enforcement measures. Together, they create a comprehensive defense system for maintaining AI privacy and security.
Training and Policy Enforcement
While technical controls and governance play a critical role in protecting data, a well-trained team is equally essential. Even the most secure systems can falter if employees aren't clear on their responsibilities. Privacy training must be a continuous process, adapting to advancements in AI and shifting regulatory landscapes. In 2025, privacy enforcement actions resulted in judgments and settlements reaching into the 8- and 9-figure range, a trend expected to persist in 2026 [11].
Privacy Training
Proper training ensures employees understand one key rule: sensitive information like personal data, client details, passwords, or account numbers should never be entered into AI tools [12]. As Just Solutions, Inc. advises:
Think of it like a public forum. If you wouldn't post it on your website, don't type it into a chatbot [12].
This simple guideline empowers employees to make quick, informed decisions about what can and cannot be shared.
Training should also highlight the differences between free, consumer-grade AI tools and enterprise solutions that offer features like data isolation and retention controls [12]. Employees need guidance on best practices, such as disabling chat histories and logging to enhance data security [12]. Tailored training sessions can be offered to different roles, such as specialized workshops for data scientists or product managers, and regular refresher courses for leadership teams [13].
To address Shadow IT risks, emphasize the importance of using only approved AI tools [12]. Training should also include anonymization techniques, like replacing names with pseudonyms (e.g., "Client A") or generalizing details before entering them into prompts [12]. Additionally, employees must understand the risks tied to file uploads, as documents often contain hidden metadata or sensitive information that may not be apparent during "drag and drop" actions [12].
Clear data classification practices further support informed and secure use of AI tools.
Data Classification Guidelines
Establishing clear data classification guidelines helps teams distinguish what can safely be processed by AI and what requires stricter handling [12]. A well-maintained data inventory, detailing sources, ownership, and formats, ensures consistent classification and improves data quality [13]. This system not only reduces errors but also boosts confidence in the insights generated, streamlining decision-making processes.
For industries bound by regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, or CMMC, ensure your AI tools comply with specific data classification needs [12]. These guidelines should be reviewed and updated annually to align with evolving state laws - currently, more than 19 states have comprehensive privacy laws, many of which include requirements for opt-out rights and automated decision-making technology [11].
Privacy Reviews in Procurement
With effective training and clear data guidelines in place, teams are better equipped to evaluate AI tools during procurement. Privacy evaluations should be mandatory before purchasing any AI tool, building on existing security and governance frameworks. This includes conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) and AI-specific risk assessments to determine how a tool handles sensitive information [11][14].
Before finalizing contracts, audit the vendor's data residency, retention practices, and third-party sharing policies [12]. Verify whether the provider uses customer data to train its models. For instance, Microsoft Copilot ensures business data is not used for training purposes [12]. Similarly, ChatGPT revised its data policies 11 times over two years to address privacy concerns, underscoring the importance of verifying vendor practices [12].
Vendor contracts should include updated personal data privacy addenda that reflect legal requirements and clearly allocate compliance responsibilities [11]. Whenever possible, opt for enterprise or business versions of AI tools. Paid tiers typically offer critical features like data isolation, retention controls, and safeguards against data exfiltration [12]. This formal procurement process helps mitigate Shadow IT risks and ensures all tools meet your organization's privacy standards before they are deployed [12].
12-Point Privacy Checklist for C-Suite Executives
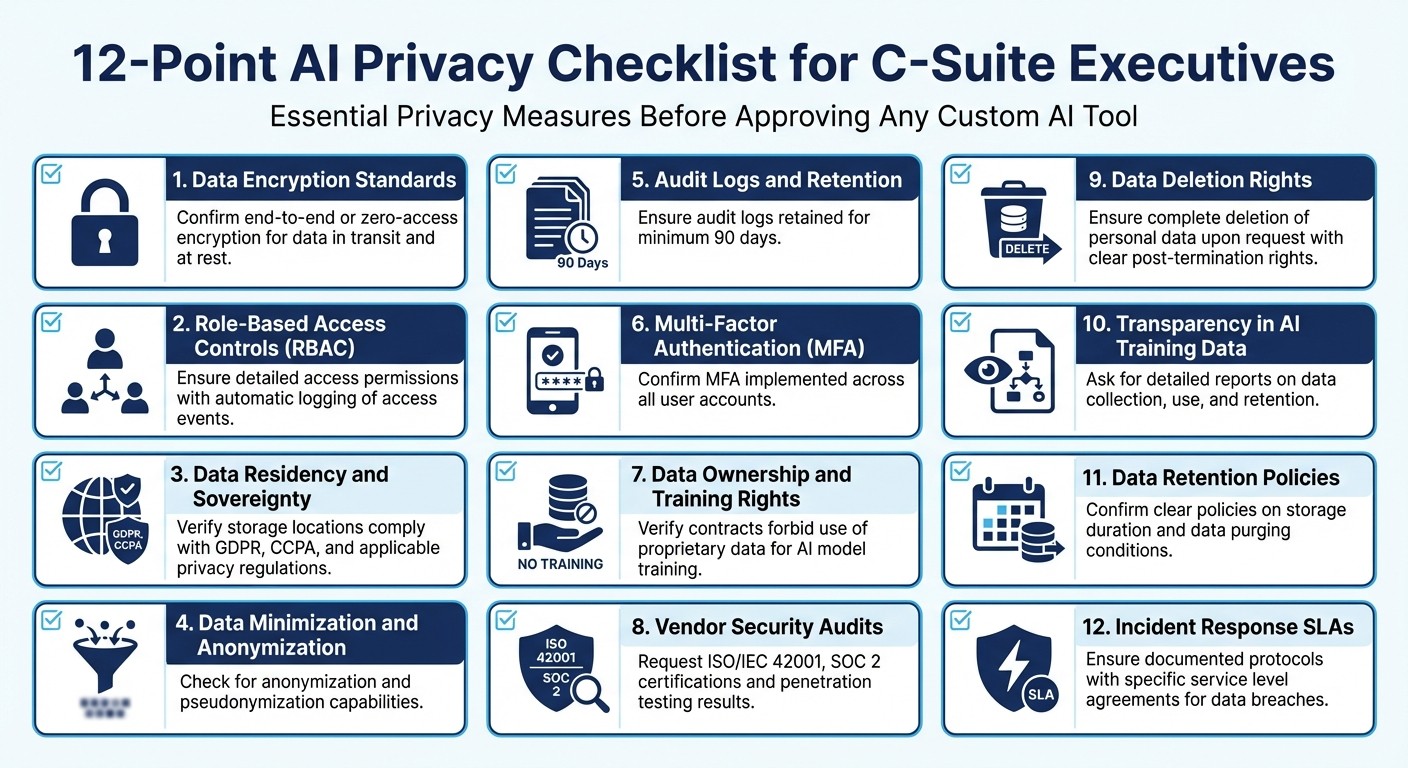
12-Point AI Privacy Checklist for C-Suite Executives
Before approving any custom AI tool, executives need a straightforward way to assess privacy readiness. This checklist outlines key privacy measures, drawing from vendor security and data management best practices. Each item is designed to help you ensure your vendor meets critical privacy standards. Review these points carefully before making any decisions.
Checklist Items 1-4
1. Data Encryption Standards: Confirm the vendor employs end-to-end or zero-access encryption for protecting data both in transit and at rest. This ensures that unauthorized access is effectively blocked [4].
2. Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC): Ensure the tool supports detailed access permissions, letting you control who can view, modify, or export sensitive data. Look for automatic logging of access events to maintain accountability [3].
3. Data Residency and Sovereignty: Verify that data storage locations comply with applicable privacy regulations, ensuring adherence to laws like GDPR or CCPA [4].
4. Data Minimization and Anonymization: Check that the tool enables anonymization and pseudonymization, such as replacing client-specific details with generic identifiers to reduce data exposure risks.
Checklist Items 5-8
5. Audit Logs and Retention: Make sure audit logs are retained for a minimum of 90 days to support compliance and investigations if needed [3].
6. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Confirm that MFA is implemented across all user accounts to add a critical layer of security.
7. Data Ownership and Training Rights: Verify that contracts explicitly forbid the use of proprietary data for training AI models. This protects your organization's data from being exploited [1][4].
8. Vendor Security Audits: Regularly assess the security practices of upstream AI suppliers. Request documentation like compliance certifications (e.g., ISO/IEC 42001, SOC 2) and penetration testing results to evaluate their reliability [1][8].
Checklist Items 9-12
9. Data Deletion Rights: Ensure the tool allows for complete deletion of personal data upon request. Contracts should clearly define post-termination rights for data retrieval or deletion [3][1].
10. Transparency in AI Training Data: Ask for a detailed report outlining how AI training data is collected, used, and retained [4].
11. Data Retention Policies: Confirm the vendor has clear retention policies specifying how long data is stored and under what conditions it is purged. These policies should align with your internal governance standards and regulatory requirements.
12. Incident Response SLAs: Ensure the vendor has documented incident response protocols, including specific service level agreements (SLAs) for handling data breaches [1].
Privacy Category | C-Suite Verification Item |
|---|---|
Data Handling | Is your data being used to train the vendor's AI model? |
Security | Does the vendor use zero-access or end-to-end encryption? |
Compliance | Does the tool meet standards like the EU AI Act or CCPA? |
Governance | Are there defined SLAs for responding to data breaches? |
Transparency | Can the vendor provide detailed reports on data collection and storage practices? |
This checklist is your final safeguard before signing any vendor agreement, ensuring that privacy concerns are thoroughly addressed and your organization remains protected.
Conclusion
Overlooking a detailed privacy review when implementing custom AI tools can expose your organization to significant risks. The 12-point checklist outlined earlier offers a structured approach to vetting vendors, helping ensure critical protections like strong encryption and responsive incident management are in place to safeguard sensitive data and maintain trust with stakeholders.
As Stoel Rives aptly puts it, "AI governance should be viewed not only as a regulatory requirement but as a business enabler" [1]. By focusing on governance, auditability, and transparency, organizations can not only meet compliance standards but also inspire client confidence and foster innovation. Incorporating privacy reviews into your procurement process ensures that innovation doesn’t come at the expense of security or accountability.
Effective AI management goes beyond governance - it demands collaboration across Legal, IT, and Business teams. Establishing a centralized AI oversight committee to create policies, audit tools, and assess models for bias ensures that deployments remain ethical and compliant with legal standards.
Organizations that prioritize these safeguards early are better positioned to succeed. Let this checklist serve as your final step before committing to any vendor agreements - because the choices you make today will determine whether AI becomes a strategic advantage or a potential risk.
FAQs
What should executives consider when evaluating the security of an AI vendor?
When examining an AI vendor's security practices, there are a few critical areas executives should prioritize to safeguard sensitive corporate data.
First, take a close look at the vendor’s technical safeguards. These should include robust encryption for both data in transit and at rest, measures to protect against network threats like DDoS attacks, and strict access controls, ideally with multi-factor authentication. These tools act as the first line of defense against breaches and unauthorized access.
Next, assess the vendor’s data-handling policies. Pay attention to how they store, retain, and dispose of data. Make sure they only collect what’s absolutely necessary and have clear, well-documented protocols for protecting that data. It’s also important to examine their third-party relationships - any subcontractors they work with should meet the same security standards and be bound by confidentiality agreements to prevent leaks or misuse.
Lastly, verify their compliance with established security standards, such as SOC 2 or ISO 27001. These certifications indicate that the vendor undergoes regular audits and has strong incident-response procedures in place. Transparency is equally important - look for vendors that offer real-time monitoring and have clear processes for notifying clients about breaches. This level of accountability can go a long way in establishing trust.
How does role-based access control (RBAC) improve data privacy in AI tools?
Role-based access control (RBAC) plays a critical role in safeguarding data privacy within AI tools. By assigning users to defined roles - like strategist, analyst, or compliance officer - and restricting their access to only the data and functions relevant to their responsibilities, organizations can enforce the “least-privilege” principle. This approach reduces the likelihood of accidental data breaches or misuse, keeping sensitive information more secure.
Another advantage of RBAC is its flexibility in managing privacy over time. When employees switch teams or leave the organization, permissions can be updated quickly to reflect their new roles. Additionally, RBAC includes built-in audit logs that record who accessed specific datasets and when, offering the transparency and accountability needed to align with U.S. privacy regulations like the CCPA/CPRA. For executives, this means data privacy risks are addressed proactively rather than waiting for issues to arise.
What key elements should an AI-specific incident response plan include?
An AI-specific incident response plan should tackle the distinct risks tied to AI models while building on the framework of a traditional cybersecurity strategy. Start by setting up governance with a cross-functional team. This team should include AI engineers, privacy officers, legal experts, and executives, each with clearly defined roles and responsibilities. Establish detection mechanisms to spot unusual model behavior, potential data breaches, or outputs that may expose sensitive information. Make sure employees have a simple and clear way to report any concerns.
In the event of an incident, the plan should detail containment steps. This could involve isolating the affected model, halting data inputs, or rolling back to a previous version to minimize damage. A thorough investigation is essential to pinpoint the root cause and evaluate the impact, particularly concerning sensitive data. The plan should also lay out communication protocols for notifying internal teams, regulatory authorities, and, if necessary, individuals who may be affected.
Finally, prioritize remediation and learning. Address vulnerabilities, retrain models as needed, document the incident thoroughly, and revise policies to minimize the chances of recurrence. Regularly review and refine the plan to ensure it stays effective as AI systems and technologies continue to advance.






